
The Lure of Triple-Net (NNN) Leases
Long leases of 10 - 20 years to tenants with investment grade covenants and fixed annual rental escalations, provide an alluring predictable cash flow stream, similar to fixed income investments.
02. February 2023
9 min. read
In the field of commercial real estate, especially in the U.S., a triple-net (NNN) lease is a lease agreement on a commercial property whereby the tenant commits to paying in addition to rent and utilities, all of the property operating, maintenance and repair expenses including real estate taxes and building insurance that would normally be paid by the property owner.
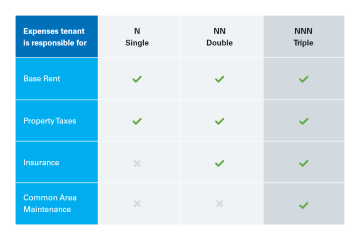
Hence these expenses are often categorized into the "three nets": i.e., property taxes, insurance, and maintenance. As illustrated in the table below, NNN leases are one of three (3) types of net leases together with single net leases and double net leases
Given triple net leased properties are typically leased to high-quality, investment grade companies with recognised brand names on relatively long lease terms (i.e. of 10-20 years), with fixed annual (or otherwise periodically structured) rental escalations that are intended to provide a hedge against inflation, such characteristics together with predictable cash flow streams and the fact tenants invest their own substantial capital into fit-outs that reduces their risk of departure and makes their occupation more “sticky”, all explain the growing lure of NNN leases to both private and institutional investors.
Especially when compared to standard single net lease agreements which are conventional in other real estate asset classes such as shopping centres and office buildings.
Two key advantages of NNN leases are that tenants have greater control over the property, which is particularly beneficial for businesses that have specialized needs or require a high degree of customization, while the typical long-term duration of NNN leases (with renewal options), ensure minimum lease-up costs and vacancy/ rental void allowances which contribute to providing stability and certainly of income for investors, similar to fixed income investments.
Despite the features of NNN leases, it is still however essential for the investor to carefully evaluate the specific terms and conditions of each lease agreement before entering into an transaction. Investors need to ensure tenants are financially stable and able to meet their financial obligations for the entire lease duration via stringent covenant analysis, while tenants equally need to determine if they are to assume the additional responsibilities and costs that come with a NNN lease and that a specific location will remain core to their needs in the future with respect to changing local demographics, road and infrastructure, risk of cannibalisation, third party competition and general micro-economic shifts.
In conclusion, triple net leases offer a predictable and stable stream of income for investors, but it remains crucial to carefully evaluate the terms and conditions of each lease before committing to a transaction.
Gross versus Net Lease
Important to note is that the term "net lease" is distinguished from the term "gross lease". In a net lease, the property owner receives the rent "net" after the expenses that are to be passed through to tenants are paid. In a “gross” lease, the tenant pays a gross amount of rent, which the landlord then uses to pay the relevant operating expenses of that property. Gross leases typically have higher rent charges to recuperate some of these expenses, as opposed to doing so through a net arrangement.
Notably, face rents are generally lower with net leases than traditional gross leases given the more expenses a tenant has to bear, the lower base rent which the owner can charge.
Triple Net (NNN) Leases in a Nutshell
A triple net lease (NNN) helps landlords reduce the risk of a commercial lease and is one of three types of net leases together with single net leases and double net leases.
A single net lease requires the tenant to pay only the property taxes in addition to rent. With a double net lease, the tenant pays rent plus the property taxes as well as insurance premiums.
A triple net lease, also known as a net-net-net lease, hence the NNN acronym, requires the tenant to pay their rent plus all three additional expenses including building maintenance costs.
Share





